90% reduction in inappropriately-initiated antifungal therapy following antifungal stewardship programme at Wythenshawe Hospital ICU
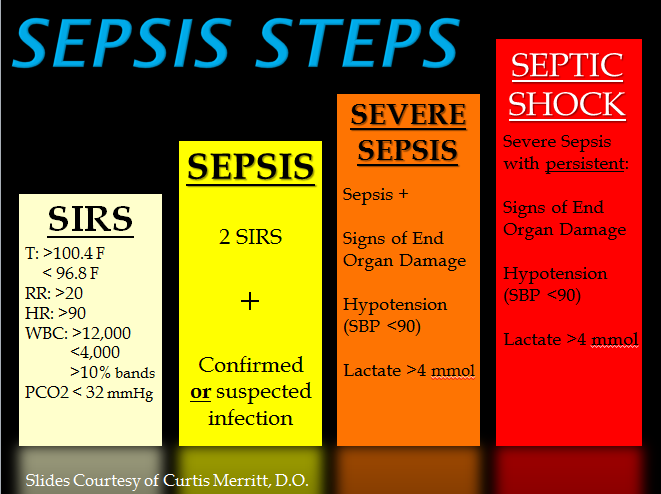
Antifungal stewardship (AFS) aims to monitor and reduce unnecessary use of antifungal agents in order to preserve their effectiveness for the future and reduce adverse outcomes for patients. A combination of reliable diagnostic techniques and appropriate guidelines for empirical therapy are vital.
Dr Riina Rautemaa-Richardson and colleagues recently implemented an AFS programme for invasive candidosis (fungal sepsis) in the intensive care units of Wythenshawe Hospital (Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust). Empirical antifungal therapy was initiated for patients with risk factors for invasive candidosis, which can be fatal. However, using serum beta-1,3-D-glucan (BDG) as a biomarker for Candida spp. in the serum, patients who tested negative had their antifungal medication discontinued.
This programme resulted in a 90% reduction of inappropriately-initiated antifungal courses, with a significantly lower mortality rate reported during the data collection period. This allowed a safe and effective reduction in the number of costly antifungal prescriptions, alongside an improvement in patient outcomes; these results highlight the need for larger, multi-institutional studies into the employment of AFS guidelines in hospitals.